Acrel Smart Home Solar: Complete Monitoring & Management for Residential PV
What is Residential Photovoltaic (PV)?
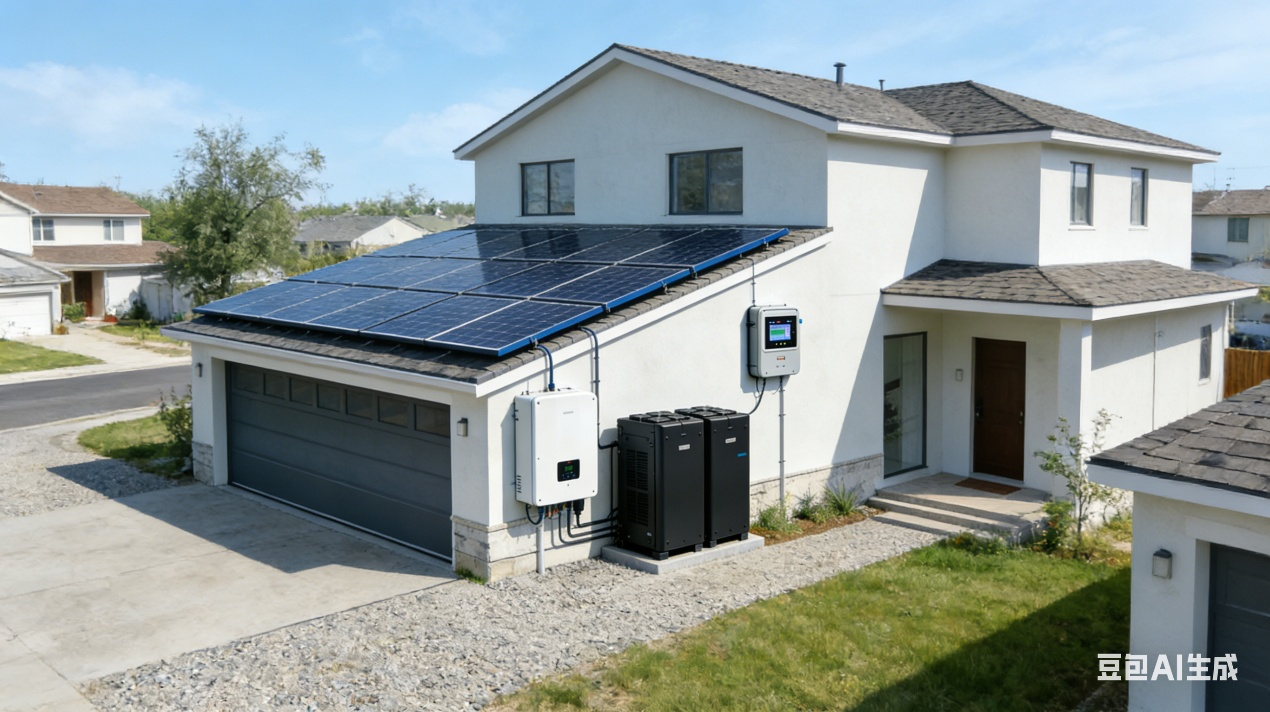
Residential PV refers to small-scale solar power generation systems installed on household rooftops, balconies, or similar areas to supply electricity directly to the home. These systems can connect to the grid and may incorporate energy storage for off-grid emergency use, representing a mainstream solution for household energy self-sufficiency.
Main Components of Residential PV: Solar panels + inverter, with optional add-ons such as energy storage batteries, monitoring equipment, and anti-backflow devices.
Operation Modes: Primarily divided into grid-tied (excess solar power can be sold back to the grid) and off-grid (the system relies solely on solar panels and batteries for power supply).
Main Customer Types
1. Ordinary Households This is the largest customer segment, commonly found in countries with high electricity tariffs and abundant sunlight. Their primary motivation is reducing electricity bills, while some also pursue energy self-sufficiency.
2. Small Farm / Ranch Owners Beyond household consumption, they need to power agricultural loads such as irrigation pumps and greenhouse equipment, often requiring multiple inverters and energy storage systems.
3. Property Developers / Property Management Companies In some European and American markets, developers integrate residential PV as a premium feature to increase property values, while property management companies install balcony solar systems for apartment buildings to attract tenants.
Core Challenges in Residential PV
1. Low Generation Efficiency & Unclear Returns
Residential PV systems often suffer efficiency losses from module shading and inverter failures, leaving homeowners unable to accurately track generation output or financial benefits.
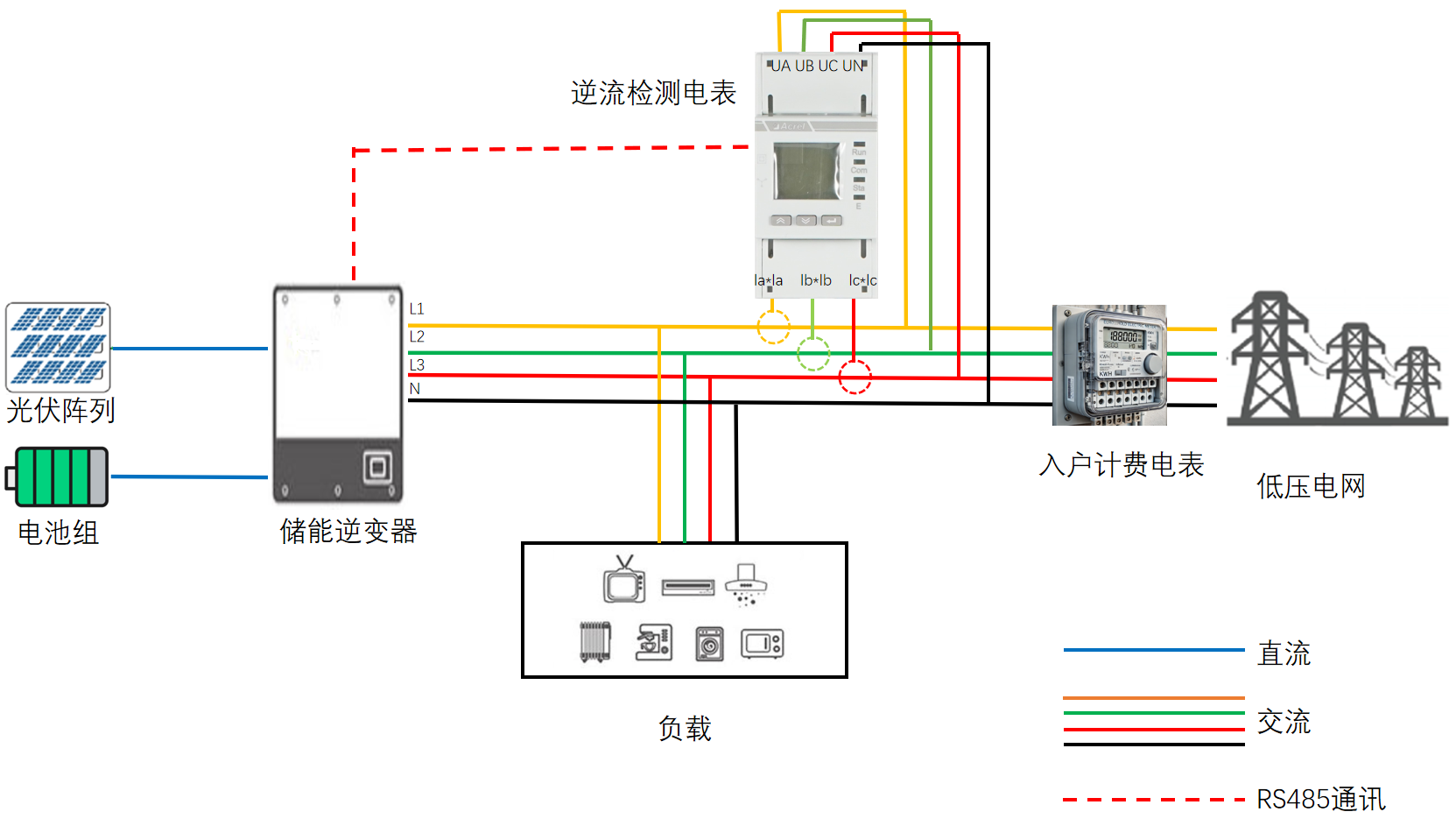
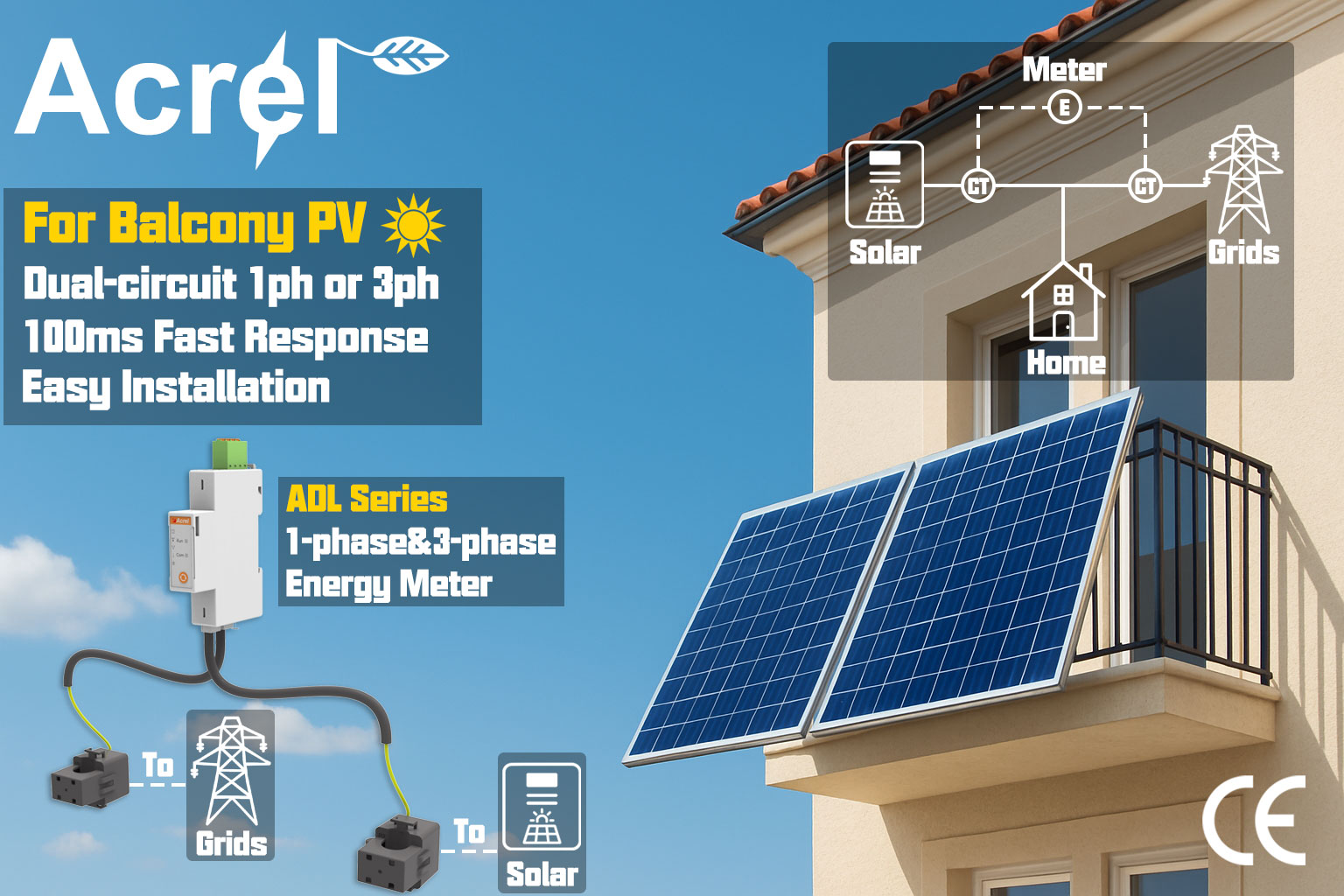
Monitoring devices provide real-time visibility into PV string production and grid interaction. The ADL200M/400M’s dual-circuit function distinguishes between direct PV supply and battery charge/discharge data, helping identify underperforming modules or faulty equipment while precisely calculating feed-in tariff revenues to eliminate profit leakage.
Residential PV systems often suffer efficiency losses from module shading and inverter failures, leaving homeowners unable to accurately track generation output or financial benefits.
Monitoring devices provide real-time visibility into PV string production and grid interaction. The ADL200M/400M’s dual-circuit function distinguishes between direct PV supply and battery charge/discharge data, helping identify underperforming modules or faulty equipment while precisely calculating feed-in tariff revenues to eliminate profit leakage.
2. High O&M Costs & Difficult Fault Detection
Residential installations are geographically dispersed, making manual inspections costly and fault detection slow.
ADL200W/ADL400W support Wi-Fi-enabled remote data upload, allowing users and technicians to monitor system status anytime via mobile apps or platforms. Automatic alerts for voltage anomalies, metering errors, and other issues enable rapid fault diagnosis, dramatically reducing O&M expenses.
Residential installations are geographically dispersed, making manual inspections costly and fault detection slow.
ADL200W/ADL400W support Wi-Fi-enabled remote data upload, allowing users and technicians to monitor system status anytime via mobile apps or platforms. Automatic alerts for voltage anomalies, metering errors, and other issues enable rapid fault diagnosis, dramatically reducing O&M expenses.
The Benefit of Residential Solar
In Southeast Asia, countries are driving solar adoption through subsidies, tax incentives, and policy liberalization, with a sharp focus on residential and distributed segments.
1. Vietnam has eased rooftop solar restrictions, purchases surplus residential solar power at fixed prices, and is advancing direct power purchase mechanisms.
2. Thailand introduced a 2025 personal income tax deduction allowing residents to claim up to 200,000 baht annually for rooftop solar installation costs, coupled with zero import tariffs on components.
3. Malaysia eliminated solar panel capacity limits, permits installation on private land, provides households with installation subsidies of up to 4,000 ringgit, and extended income tax exemptions for solar leasing companies until end-2026
Post time: Dec-12-2025